Published
- 09:00 am

BCI Finance (via the fintech-focused BCI Credit Opportunities Fund) and Ferovinum are pleased to announce the launch of a new funding facility to enable Ferovinum to materially increase the scale of its support for the wine and spirits industries.
Ferovinum provides capital against wine and spirits inventories, using its tech platform to enable customers to upload inventories to access funding, manage their stock holdings and supply chain logistics, and manage cashflows associated with trade receivables.
This innovative solution to alleviate the capital and logistical burden of inventory-intensive industries was the perfect fit for fintech specialist lender BCI Finance.
BCI Finance Managing Director Sam Kemp comments, “At BCI Finance, we are passionate about working with truly innovative lending businesses that are on a mission to disrupt their industries. We believe that the Ferovinum platform has the ability to modernise an antiquated, fragmented global supply chain, while levelling the playing field in enabling smaller and independent producers to access funding in a way that had previously been the privilege of select larger players. We’re delighted to be supporting Ferovinum and to be deploying capital into its sector, and we look forward to continuing to work with the business as it moves through the next phases of its growth.”
This facility has been setup to bridge into Ferovinum’s upcoming multi-tranche facility and will support senior lending for Ferovinum’s next £100m of capital deployed into wine and spirit supply chains.
Ferovinum’s Mitch Fowler added, “BCI Finance were extremely impressive to work with. They immediately understood our business model and worked with us to design a bespoke financing package to support our rapidly growing customer book. The process was quick and efficient from start to finish and BCI has the scale and flexibility to continue to support our rapid growth profile.”
Related News
- 09:00 am

The Group is among the first in Italy to achieve "carbon neutrality" thanks to
the sustainable initiatives already implemented in recent years,
the current carbon mitigation plan and the financing of some international projects
to offset residual emissions in cooperation with Lifegate.
The Sella group writes off the impact of CO2 emissions ahead of the plan set for 2024. Achieving this target was the result of sustainable initiatives dedicated to the reduction of its carbon footprint already implemented in recent years, a plan for further mitigation of emissions and joining the "Zero Impact" project of Lifegate, aimed at significantly mitigating the environmental impact of Group companies and offsetting residual emissions. This project supports internationally certified initiatives to absorb CO2, protect the environment, promote the circular economy and support local communities.
Sella is thus among the first groups in Italy in the banking and financial sector to reach the so-called "carbon neutrality". The path to reach "carbon neutrality" started with an in-depth analysis of CO2 emissions based on those produced by the Sella group in 2019 before the COVID-19 health emergency required the rethinking of working methods through the use of smart working and remote relations. This measurement quantified the annual production of the Group in Italy and abroad as approximately 13 thousand tons of CO2 equivalent.
The zero-setting intervention, concerning the impact of CO2 emissions produced from now to the next three years, involves specific areas of application: direct emissions and emissions attributable to activities within the company (such as gas consumption for heating, or fuelling the company fleet); indirect emissions from the internal energy consumption of buildings (such as purchased electricity) and other indirect emissions related to corporate activities (such as those concerning the business transfers of employees or the purchase of office equipment and devices).
The main environmental sustainability initiatives of the Sella group
The headquarters in Biella, in particular, were built following modern criteria of eco-sustainability and reduction of the environmental impact involving the installation of photovoltaic systems and a solar thermal plant for the production of hot water. In addition, the S32 building in Milan, which houses the Fintech District community, has obtained the LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) "Platinum" certification, the highest level for buildings that make efficient use of energy resources.
Starting from 2020, the Sella Group has also launched the "Sustainability Project" with the dual objective of constantly improving its social and environmental performance and being the promoter of a sustainable economy, supporting its customers in the transition process to an effective ESG-impact economy. In light of the above, Banca Sella has allocated a ceiling of one billion euros to finance projects by companies doing their best in making a tangible impact on the 17 Sustainable Development Goals of the United Nations 2030 Agenda.
The "Sustainability Project" allowed for several initiatives of further mitigation. These involved the use of office materials with low environmental impact, the use of FSC-certified paper, the installation of free water dispensers at the headquarters of the Group, the distribution to employees and co-operators of eco-sustainable water bottles equipped with an embedded chip providing through an app the amount of plastic saved at every refill, and the provision of training for a "sustainable" diet. Other significant initiatives include the gradual replacement of vehicles in the company fleet with “green” models and the launch of a forestry project in Italy.
The Group is also carrying out the project for a run-of-the-river hydroelectric plant in Biella, which exploiting two geodetic jumps available, will mitigate the hydrogeological risk and increase the use of energy produced from renewable sources.
The LifeGate “Zero-Impact” project
The Sella group has chosen the LifeGate “Zero Impact” project to implement the three-year process of reducing its carbon footprint and offsetting CO2 equivalent emissions. The protection of growing forests, and the development of energy efficiency and renewable energy production projects, made it possible to counterbalance unavoidable residual CO2 emissions under the Kyoto Protocol.
The Sella group, through the purchase of carbon credits, is already supporting three specific initiatives in Europe, Africa and Central America, certified by international bodies, whose performance will be continuously under monitoring:
- in Romania, a project is in place to reduce emissions related to plastic recycling. The first certificate for compensation in Europe is underway, which use PET waste for recycling by significantly cutting down (up to 48%) the greenhouse gas emissions that would come from the production of plastic products;
- The project in Zimbabwe focuses on the protection of the Kariba forest. Since 2011, nearly 785,000 hectares have been preserved from deforestation and soil degradation, avoiding the release of over 3.5 million tons of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere every year;
- The initiative in Guatemala aims to protect the landscape of the Caribbean coast of the state (almost 60 thousand hectares) and reduce greenhouse gas emissions by fostering ecosystem conservation and practical and sustainable economic activities.
Related News
- 02:00 am

Prior to non-fungible tokens, it was extremely difficult to create digital exclusivity for assets. Despite copyright measures in place, consumers may simply replicate or steal digital artwork. The development of NFTs has enabled the production of crypto art and digital valuables, but it doesn't stop there. NFTs may be used to verify the authenticity of a wide range of one-of-a-kind and collectable items, ranging from real estate to logistics.
What is NFT?
Non-fungible tokens, or NFTs, are blockchain-based cryptographic assets that possess distinct identification codes and information that separates them from one another. They cannot be sold or traded for counterparts, unlike cryptocurrencies. In comparison, fungible tokens, such as cryptocurrencies, are replaceable and may be used as a means of exchange.
While the NFT ecosystem is still in its infancy, there are a number of fascinating efforts to look into, some of which are already providing considerable value to creators and consumers. Eager trading enthusiasts can trust BitiQ App for a variety of cryptocurrencies to invest in.
Art NFTs
Crypto art is a virtual currency that can be copied and verified digitally. The entirety of the value of crypto art is derived from digitally verifying its authenticity and ownership. We can't demonstrate we own the original CryptoPunk since it's available on the Ethereum blockchain for anybody to access or keep. As a result, crypto art is one of the most widely used NFT applications.
Collectible NFTs
An NFT may be both a collectable and an art piece, and crypto art can be both. Each NFT is signed using just the verified creator's Twitter @handle, guaranteeing that only the original creator may mint them. This method creates a limited-edition digital collectable that may be exchanged or preserved. It's simply a digital reproduction of a handwritten autograph. Purchases on NFT markets such as Opensea, BakerySwap, and Treasureland account for a sizable portion of revenues.
Finance NFTs
It's easy to forget that not every NFT is based on a song, photograph, or collectable object. NFTs also provide significant financial advantages in decentralised finance (DeFi). JustLiquidity is a decentralised financial platform that enables users to stake a pair of coins in a pool for a certain period of time in return for an NFT that permits them to enter the next pool. The NFT serves as an entrance ticket and is erased once you've moved on to the next pool. This technique generates a secondary market for these NFTs because of the access they provide.
Gaming NFTs
In gaming, unique tradable and purchasable products are popular. Their scarcity directly affects their worth, and gamers are already accustomed to the notion of valuable digital items. Microtransactions and in-game purchases have given rise to a multibillion-dollar gaming business that may profit from NFTs and blockchain.
Music NFTs
To create a collectable piece of music, link audio to an NFT in the same manner that you would attach a photo or video. Receiving a fair share of royalties from their work is a real problem for artists. However, there are at least two approaches for obtaining a proportionate outcome: blockchain-based streaming networks and blockchain royalty monitoring. Competing for streaming services like Amazon Music or YouTube is difficult for tiny blockchain businesses. Even when a behemoth like Spotify purchased MediaChain, a blockchain royalties system, artists received no substantial advantages.
Real-world asset NFTs
The use of NFTs to connect physical assets can assist in digitising the way we authenticate ownership. When a product is connected to an NFT, owning the NFT can be as significant as having the asset. You may also embed the NFT within an item using a physical cold storage wallet. As the Internet of Things evolves, more NFTs will most likely be used to reflect physical assets.
Logistics NFTs
Because of its irreversibility and integrity, blockchain technology has the potential to be useful in the logistics industry. It is important to know where food, goods, and other perishable items have been and how long they have been there. There are various options for integrating NFTs into the supply chain. At each level of the chain, they all require the use of the same foundation.
Closing thoughts
With the growing popularity of NFTs, there's a good chance we'll see many more concepts and uses in the future. For the time being, not every NFT application has had the opportunity to progress beyond an idea or a small experiment. Some of these could be ineffectual or unpopular. When it comes to more fundamental and straightforward problems, such as the shortage of art and collectables, NFTs are certainly here to stay.
Related News
- 03:00 am

With Finastra’s Fusion Phoenix and a suite of ancillary solutions, Workers Credit Union is maximizing opportunities to grow beyond its traditional offerings and deliver on its mission to improve member financial wellness
Finastra today announced that Workers Credit Union has selected Fusion Phoenix as its new core banking solution to grow its membership, future-proof its business and strengthen its position against competitors, including digital banks. In addition, it will use Fusion MortgageBot, Fusion ECM, Fusion Originate, Fusion Analytics, Fusion Treasury Essential and other Finastra solutions to bolster its offerings.
“Our unique commitment to serving our members as they work toward their financial goals has positioned us for unprecedented growth,” said Doug Petersen, President & CEO, Workers Credit Union. “We recognize that to best serve our members we need to continue to add new products and services. With Fusion Phoenix, bringing new services to market will be quicker and easier, and the core will be able to grow with our needs as our membership continues to expand.”
With the Fusion Phoenix open core, Workers Credit Union will also experience increased speed to innovation and, by unlocking the power of data, will be able to proactively engage with members through personalized services. It will realize improved efficiencies through Fusion Phoenix’s intuitive Microsoft-based architecture and its embedded workflow manager, which allows common tasks and processes to be defined and automated. Finastra was also able to demonstrate that the migration to its solutions would establish a predictable cost structure for the credit union and allow it to grow its membership without incurring additional costs.
“The decision to switch core vendors is never easy, but Finastra was able to provide both near and long-term benefits for Workers Credit Union and its members, making that choice much simpler,” said Chris Zingo, SVP and GM of Americas Field Operations, Finastra. “By adding other products from Finastra — addressing lending mortgage and treasury needs — Workers Credit Union isn’t only acquiring a suite of fully-integrated, best-of-breed solutions, but is also positioning itself to expand into new lines of business and realize new revenue streams.”
In addition to its new core, Workers Credit Union selected Fusion Originate to grow its commercial loan portfolio and Fusion Treasury Essential to monitor cash positions. The selection of Fusion Treasury Essential marks the first time the treasury solution was sold to a credit union and demonstrates Workers’ visionary approach to how it can leverage available tools to differentiate itself and grow in new strategic directions.
Related News

Rabi
Senior director at Infosys
Industry cloud is a public cloud service offering that has been heavily customized to fit a specific industry in order to accelerate business transformation & accommodate sec see more
- 03:00 am

Binance, the world’s leading blockchain ecosystem and cryptocurrency platform, has today announced the appointment of Mark McGinness, former Head of International Relations at the Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA), who joins the organization as its Chief Regulatory Liaison Officer.
Following a commitment to lead the industry in working more closely with regulators as it charters a path forward to become a financial institution, Binance has grown its international compliance team and advisory board by 500% since 2020. Recent appointments include Greg Monahan, former US Treasury Criminal Investigator, as Global Money Laundering Reporting Officer (GMLRO); as well as Tigran Gambaryan and Matthew Price, both former Special Agents of the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), as Global Intelligence and Investigations and Senior Director of Investigations, respectively.
Mark has over three decades of experience as a leading financial services regulator, working with industry stakeholders, international regulators and regional securities and insurance commissions. In Mark’s previous role leading international engagement for the DFSA, he was instrumental in establishing a global network of over 85 regulators and settled 100 Memoranda of Understanding for the financial center. Mark also held the position of the DFSA’s Chief Decision Maker, deciding on matters referred by its Enforcement division.
Prior to joining DFSA, Mark was Head of International Relations and Advisor to the Chairman of the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC), where he was responsible for its international engagement and advising on ASIC’s commitment to global standard-setting. Mark has also held advisory positions as a subject expert for the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank.
“Mark is one of the most respected regulators and compliance experts in the industry. He brings with him over 30 years of invaluable experience working alongside key stakeholders in the financial services industry," said Binance CEO ‘CZ’ Changpeng Zhao. “Mark joining our leadership is not only a huge step forward for Binance, but the industry as a whole, as we work to grow the industry responsibly with the support of regulators and policymakers across the globe.”
“The rapid mainstream adoption of blockchain and crypto technology signals a need for a deeper understanding and appreciation among governments, regulatory bodies and users alike,” said Mark. “I aim to bridge this divide through working closely with industry leaders and policymakers to not only set best practices and regulatory frameworks, but also broaden their understanding of this dynamic industry.”
Related News
- 01:00 am

Innovations in sustainable finance and digital transformation, alongside important initiatives in transparency and regulation, will help reinvigorate Africa’s financial markets as they recover from the impact of Covid-19, according to research in the latest African Financial Markets Index from Absa and OMFIF.
- Out of 23 countries in the index, 19 score lower than last year. This decline reflects more difficult market conditions, methodological changes and the inclusion of environmental, social and governance indicators in the index. Despite the fall in scores, few examples reveal an underlying deterioration in the policy, regulatory or developmental environment in any of the index countries.
- The inclusion of ESG initiatives in the formal scoring highlights important developments and opportunities in this area, though at the cost of impacting the scores of those countries for which work is at an early stage. Only 13 countries in the index have ESG-focused policies in financial markets and nine countries have introduced sustainable finance products.
- South Africa, Mauritius and Nigeria maintain their lead in the index, though with scores slipping in 2021 for all three.
- Ghana and Uganda enter the top five for the first time, both earning points for progress in Pillar 6: Enforceability of standard master agreements.
- Nigeria gains the lead in Pillar 3: Market transparency, tax and regulatory environment. Namibia maintains its lead in Pillar 4: Capacity of local investors, while Egypt tops Pillar 5: Macroeconomic opportunity. South Africa remains on top for Pillar 1: Market depth and Pillar 2: Access to foreign exchange. It ties for first with Ghana and Nigeria in Pillar 6: Enforceability of standard master agreements.
The index measures financial market development in 23 countries from across the African continent, highlighting economies with the most supportive environment for effective markets. The aim of the index is to show how economies can improve the market framework to bolster investor access and sustainable growth, and act as a benchmark for investors and policy-makers.
As a reflection of the global push towards sustainability, this is the first year that the index has included ESG indicators. The availability of sustainable finance products, such as green bonds and equities, now contributes to countries’ scores for Pillar 1: Market depth. The index also scores countries on policies that promote ESG initiatives in financial markets for the first time.
The introduction of these sustainability-focused indicators weighs down the scores for many countries in the index as developments in this area are often at an early stage. The average score in the index fell to 46.4 out of 100 in 2021 from 50.8 in 2020, reflecting markets’ muted performance in these new indicators. However, the new measures serve as targets for countries to work towards.
Charles Russon, chief executive of corporate and investment banking, Absa, said of the index’s findings: ‘While some might find it disheartening to see the average score across the board drop, Africa is navigating an extremely tricky economic atmosphere. Recovery from the Covid-19 pandemic has not been as straightforward as we would have hoped last year, and this has had a large impact on the twin challenges the continent faces in reinvigorating financial markets post-pandemic, while strengthening market infrastructure.’
‘However,’ he continued, ‘We’ve seen a lot of positive progress in countries’ efforts to upgrade market infrastructure and regulatory support through the development of technology-based tools which will help future-proof Africa’s financial markets. With countries using innovation to boost local markets and build a broader investor base, there are plenty of reasons to be hopeful about the future of Africa’s macroeconomic landscape.’
In Pillar 1: Market depth, scores dip by an average of 1 point to 40.5 from 41.5 in 2020 due to lower equity market turnover, which has persisted since the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic. While market capitalisation rose in almost all of the countries in the index, it was not enough to offset weak trading activity. Only nine countries have introduced financial products that can be classified as ‘green’ or ‘sustainable’, with green bonds available in seven countries, either on exchanges or over the counter. Kenya and Morocco score highest in this indicator for having green or sustainable bonds, equities and mutual funds in their markets.
Foreign exchange reserves grew by 24% in Pillar 2: Access to foreign exchange, with South Africa coming first and Eswatini moving up 11 places. However, a lack of liquidity in the FX markets, as measured through interbank figures, weakened across almost all countries.
Nearly all countries’ scores declined in Pillar 3: Market transparency, tax and regulatory environment due to lower marks in capital market development. Poor performance on the new indicators that look at incentives for issuance of sustainable financial instruments, integration of sustainability factors in financial market standards and adoption of climate stress testing also contributed to the decline.
Namibia tops Pillar 4: Capacity of local investors once again, earning full marks for having a deep pension market relative to the size of its population and securities market. However, weak potential on the part of the domestic pensions market meant that 19 countries failed to score over 50.
Countries generally performed best in Pillar 5: Macroeconomic outlook, achieving an average score of 62. Egypt regains the lead – which it lost to South Africa last year – propelled by strong gross domestic product growth in 2020. The macro impact of the pandemic continues to be felt in this sector with economic growth for many countries subdued and public finance showing strain.
Ghana, Nigeria and South Africa earn full points in Pillar 6: Enforceability of standard master agreements. Mauritius, Uganda, Zambia and Malawi miss out on joining these countries at the top of the pillar by not yet fully adopting standard master agreements.
‘The index is evolving to stay relevant, recognising the greater role that sustainability plays in market development, as well as the importance of mitigating climate-related risks to the financial system, especially for African countries that are more vulnerable to the effects of environmental deterioration,’ said David Marsh, chairman of OMFIF. ‘Innovations in sustainable finance and market infrastructure will be critical to ensuring that African markets remain competitive and future-proof.’
Related News

Garry Jones
CEO at NovaFori
Carbon credit trading is playing an increasingly important role in supporting green initiatives and helping companies meet ambitious goals for reducing greenhouse gases see more
- 05:00 am
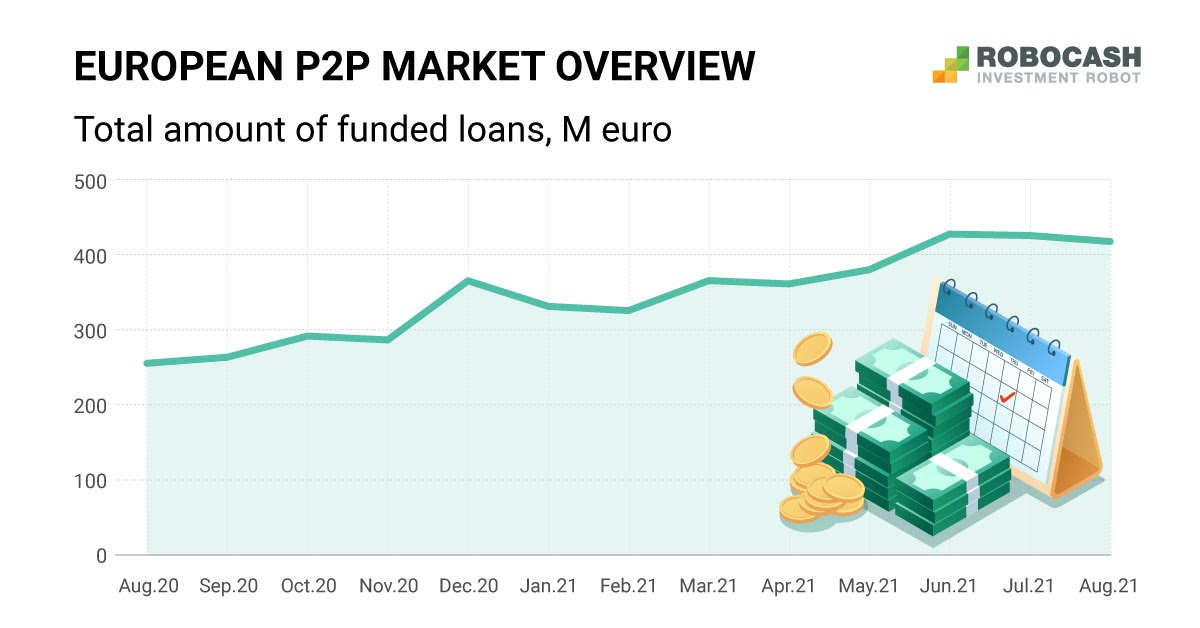
To assess the growth rate of P2P platforms, Robocash analysts studied 43 platforms that are present in 16 European countries and operating mainly in the consumer and business segments.
The funding volume on platforms of Belgium, Bulgaria, the Czech Republic, France, Ireland and Croatia has grown by an average of 16% over the past year*. What these P2P players have in common is that, on average, they fund loans of 3 to 14 M euro per month and have a long track record.
The Polish platforms passed the coronavirus period most easily, with a maximum drop of 11% in the acute period . “This trend could be explained by the low market presence. On the one hand, it reduces the risks of a sharp downturn, but on the other hand, it also limits growth opportunities”. - comment on the situation Robo.cash analysts.
A sharp decline and high growth after the main wave of the coronavirus was observed by the Belgian platforms. “It is possible that such dynamics happened due to the small volumes and high volatility of these platforms. - add specialists. "These platforms easily react to any positive or negative trend in the market, because of which panic could have a strong impact. However, the volumes would return to the previous level as the market recovers."
In general, the influence of the registration locality on the activities of the P2P platform itself is low. In part, this can be expressed in the population characteristics, if the platform operates directly within the country and issues loans to its citizens or businesses.
“Regardless of where the platform belongs geographically, the market is largely driven by general trends. However it is very likely that the P2P platforms of the countries noted above will continue to develop at an outstripping pace. Thus, in August 2021, Robo.cash volumes increased by 139% compared to August 2020, representing the Croatian market trend,, which is higher than 63% of European P2P platforms", - the analysts summarize.
* for the year, the period from August 2020 to August 2021 is taken
Related News

Elina Mattila
Executive Director at Mobey Forum
Having already swept through numerous industries around the world, the sustainability revolution is now taking the banking sector by storm. see more









