Payment Trends for 2018

- Ralf Ohlhausen, Business Development Director at PPRO
- 05.02.2018 07:00 am undisclosed
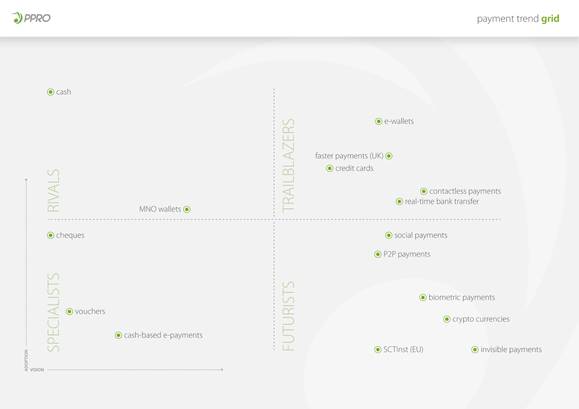
From IoT to peer-to-peer offerings, the PPRO Group - specialists in cross-border electronic payments - have predicted key online payment trends for the year ahead. With digitisation in the world of payments progressing by leaps and bounds, the following seven developments are expected to make waves in 2018.
Internet of Payments
According to Gartner, the number of devices connected to the Internet of Things (IoT) is set to increase from 6.4 billion in 2016 to 20.8 billion in 2020. Consumers are increasingly expecting their IoT devices to enable more than just carrying out tasks automatically; they also expect them to facilitate payments. For example, consumers with connected fridges can expect to see depleated items restocked and automatically paid for. Visa is also working with Honda to develop technology that can detect when a car’s petrol is low and enables users to pay for a refill using an app that is connected to the in-car display.
Context-Based Payments
Anyone heading to the checkout, whether with a real or virtual shopping basket, often takes a moment to decide whether their purchase is really worth it. Integrating payment into the context of the shopping experience and transaction can help remove this barrier to sale. It renders the POS almost invisible, while the payment process runs automatically in the background of a shopping app being used.
Wireless payments – a concept already being implemented more frequently online – will also be used in brick and mortar stores. Customers will, in the future, no longer need to reach for their cash or a credit card; instead, they can pay wirelessly in passing – whether from their smartphone via Bluetooth, using the RFID chip in their debit card, or automatically by facial or voice recognition. This will make the transaction seamless, and leave little time for consumers to rethink their purchase.
Peer-to-Peer Payments
In 2018 payment processes will be increasingly integrated into peer-to-peer (P2P) systems. In India, for example, WhatsApp users can already use P2P payments to send money to friends during online chats. Apple is also implementing this feature with Apple Pay Cash. The new voice input technologies, such as Alexa, Siri and Cortana, mean that P2P payments and banking transactions can also be carried out using voice commands.
Real-Time Payments
The push pay model makes real-time payments possible. Thanks to the SEPA Instant Credit Transfer (SCT Inst) scheme, the requisite European infrastructure has been in place since 21st November 2017. In Germany, it is already supported by the UniCredit Bank, the Deutsche Kredit Bank, and many savings banks. But it will probably be some time before the majority of banks are using the new system – perhaps not until participation becomes mandatory.
In 2018, however, additional German participants are expected to join the scheme as market pressure increases. It will be interesting to see the extent to which SCT Inst will open up new payment methods and how much retailers, in particular, will take advantage of the speed and reliability of real-time transfers to convert their processes to genuine real-time transactions.
Partnership between Banks and Fintechs
The technical specifications (Regulatory Technical Standards, RTS) defined by the European Commission for the new Payment Service Directive, PSD2, represent a major compromise between the interests of the established banking industry and the European FinTechs.
From the FinTech point of view, it would have been better to offer them the same as banks, and a free choice of using APIs or access via online banking. This would have resulted in good APIs being used while poor ones were ignored, creating a kind of self-regulation. At least, however, the new version is less of a threat to the European FinTech sector than the original version issued by the EBA at the end of February 2017. This is expected to result in a solid foundation which will foster increased competition and security in payment processes, which will provide both retailers and consumers with more choice and information monitoring.
Decentralisation through Blockchain Technologies
The technological basis for Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies will facilitate the creation of more innovative financial solutions in 2018. Institutions will use blockchain technology to establish direct connections, thus eliminating the need for intermediary or correspondence banks.
Nasdaq has already created a platform which allows private companies to issue and trade shares via blockchain. Here, the complete trading process – from execution to clearing to settlement – takes place almost in real-time, while the technology allows traceability. Blockchain can also be used by regulators as a completely transparent and accessible recording system, thus making auditing and financial reporting considerably more efficient. The number of uses for blockchain is constantly increasing and, although the technology has not yet actually achieved breakthrough status, like many radical technological shifts, it needs time to establish itself.
Commercialisation of MNO Wallets
More than two billion people globally currently do not have access to financial services. In many countries with low financial inclusion, peer-to peer-payments through mobile wallets or mobile network operator wallets (MNO wallets) are the norm. With growing popularity of e-commerce in these countries comes the commercialisation of such wallets for B2C payment methods. There is a clear shift from P2P payments to B2C payments seen in many Asian, African and Latin American countries.





















